Going digital is the way of the modern world. With time things change and so does invoicing. In Saudi Arabia, E-invoicing is framing the financial landscape led by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA). This way of invoicing helps in many ways like from fraud, in transparency, and easier tax compliance for businesses in Saudi. Let’s get to know more about ZATCA- E-invoicing in Saudi Arabia.
What is ZATCA E-Invoicing in Saudi Arabia?
ZATCA e-invoicing is basically a digitized system (also known as FATOORAH) requiring businesses subject to VAT in Saudi Arabia to issue, store, and exchange invoices electronically. It helps in avoiding paper invoices (that can be misplaced) and switching to the more secure way. With e-invoicing there is a very less chance of misplacement of the invoice which offers easy accessibility and security.
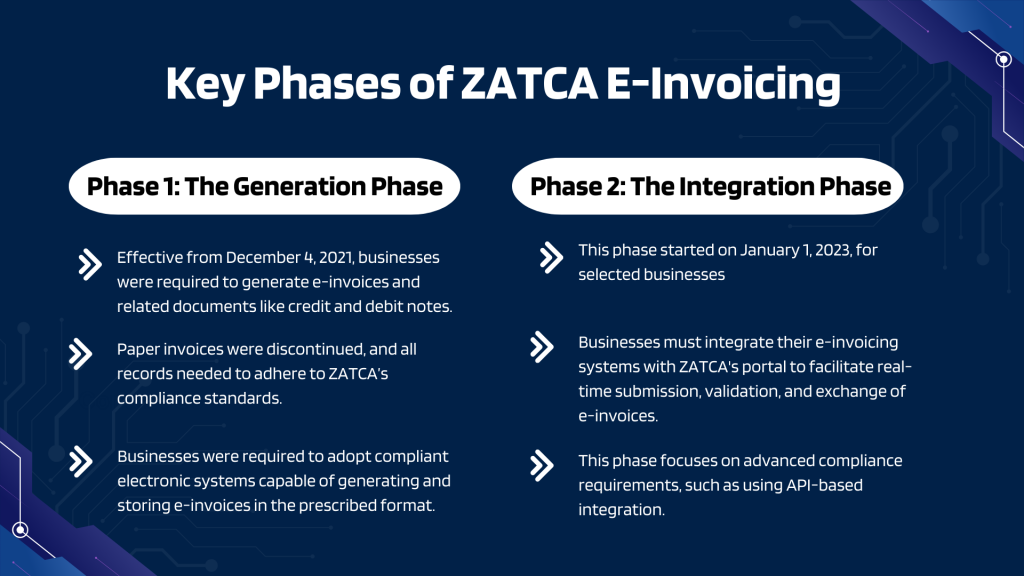
Types of E-Invoicing in Saudi Arabia
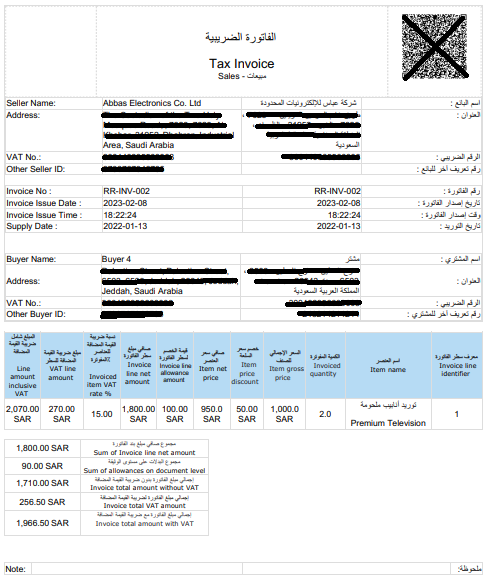
1. Standard Tax Invoices
Issued by B2B (Business to Business) or B2G (Business to Government), Standard Tax Invoice contains all the sections of tax invoice, most importantly VAT registration number of either buyer or seller. It helps customers in claiming input VAT deduction.
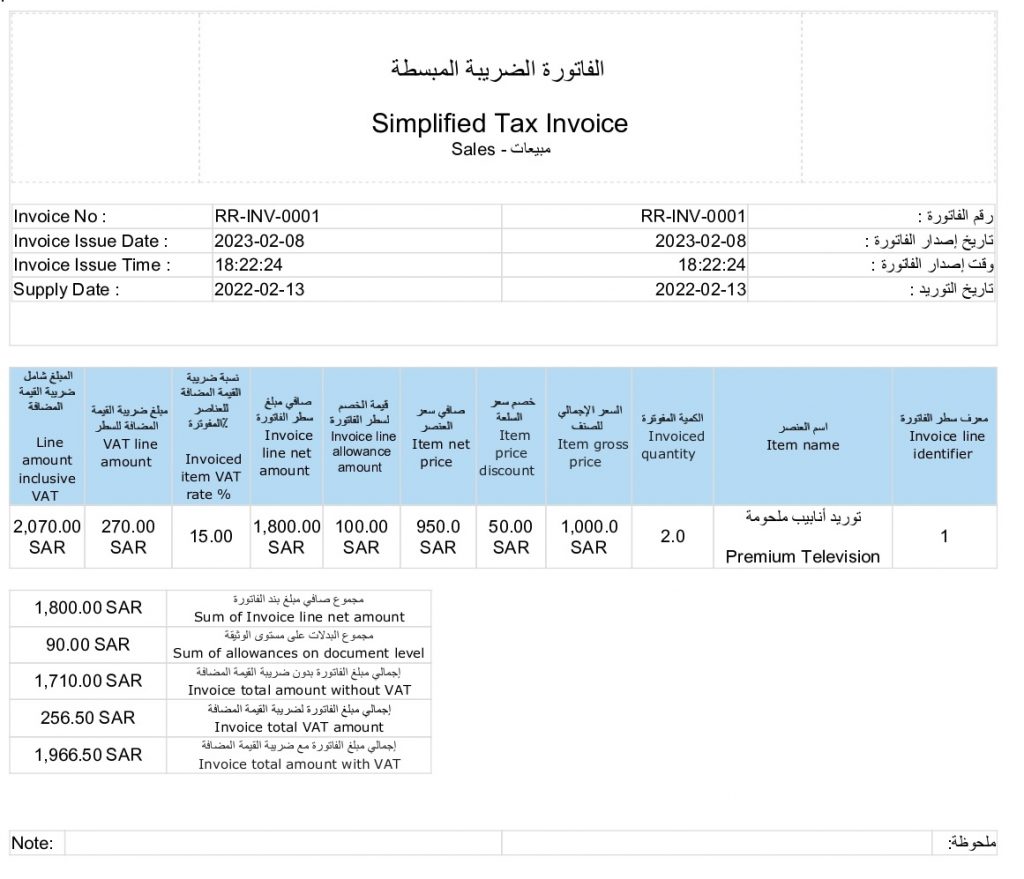
2. Simplified Tax Invoices
Issued by B2C (Business to Customer), Simplified Tax Invoices contain the main elements of tax invoice. A buyer cannot claim VAT deduction here. In Phase 1, it can be simply shared with customers but in Phase 2, it must be reported to ZATCA within 24 hours.
Scope of e-Invoicing in Saudi Arabia
E-invoicing in Saudi Arabia is reshaping how businesses handle their financial transactions. It encompasses all VAT-registered businesses, including third parties responsible for issuing invoices. Covering industries like retail, construction, hospitality, and logistics, it facilitates both B2B and B2C transactions. This initiative by ZATCA simplifies tax compliance, ensures fairness, and fosters accountability in financial dealings. Additionally, it aligns with the goals of Vision 2030, steering the country toward a more transparent and digitally advanced economy.
ZATCA e-Invoicing Compliance Guidelines
There are some guidelines you need to follow before you switch to e-invoicing:
– All taxable goods and services that are subjected to VAT is applicable to the e-invoicing provision
– Language is also a guideline. All the invoices must be issued in Arabic Language. A translation is acceptable, but the invoices must include Arabic.
– All businesses that are VAT-registered should have an e-involving system for sales. Any other third party that is issuing tax invoices on the behalf of the person who is taxable should also comply.
– Format of invoices: XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) format
– Other than B2B, B2G, and B2C transactions, e-invoicing must be implemented in debit note and credit note.
– Integrate your system with ZATCA portal (It is mandatory)
– Securely connect your system via API and make UUID and a digital signature. (API- Application Programming Interface and UUID- Universally Unique Identifier)
Benefits of ZATCA E-Invoicing
– Increased Transparency: It helps in avoiding frauds and tax evasion with the help of a tamer-proof system. It provides transparency in transactions, helping government with making tax compliance better.
– Efficiency in Business Operations: It helps in automating invoicing processes which lead to reduced paperwork, and speed in transactions.
– Improved Accuracy: It also helps in minimizing human errors through automated processes.
– Environmental Benefits: It also helps in reducing paper use which is a step to saving environment.
E-Invoicing Penalties for Non-Compliance
The penalties are applicable on the basis of the nature of the offence. Mostly, the first offence is dismissed with a warning, but multiple times can lead to penalties. Let’s get to know about penalties in ZATCA E-invoicing:
– Not archiving invoice or not issued invoice: SAR 5,000 to SAR 50,000
– Wrong Amendments or e-invoice cancellations: SAR 10,000 to SAR 50,000
– Missing QR/ No reporting on failure of system/ No VAT registration number of the buyer: Warning
Repeated violence can result in the penalty of SAR 1,000 which keeps increasing if the changes are not made.
Conclusion
ZATCA E-invoicing in Saudi Arabia is one of the major steps towards digital transformation in Saudi Arabia. This e-invoicing system helps businesses with operational efficiency, reduce risks, and contribute to a transparent economic ecosystem. The above article is a comprehensive guide to e-invoicing. If you were someone looking for this information, hoping this article was helpful to you.
Important Reference Links:
https://zatca.gov.sa/en/E-Invoicing/Pages/default.aspx
https://zatca.gov.sa/en/pages/default.aspx
https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-benefits-of-Zatca-approved-e-invoicing-in-Saudi-Arabia
https://www.quora.com/Is-e-invoicing-will-be-mandatory-in-Saudi-Arabia
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-e-invoicing-rollout-in-Saudi-Arabia
FAQs
1. What is ZATCA e-invoicing?
ZATCA e-invoicing is a system introduced by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority in Saudi Arabia, requiring businesses to generate, store, and exchange invoices electronically. It aims to ensure compliance, reduce tax evasion, and promote transparency in financial transactions.
2. Who is required to comply with ZATCA e-invoicing?
All VAT-registered businesses in Saudi Arabia and third parties issuing invoices on their behalf must comply with the e-invoicing regulations.
3. How can businesses prepare for Phase 2 of e-invoicing?
Businesses can prepare by upgrading their invoicing systems to ensure compliance with ZATCA standards, integrating with ZATCA’s platform, and ensuring their invoices include all mandatory details.
4. Is training required for staff to manage e-invoicing?
Yes, businesses should provide training for their staff to understand the requirements and use compliant invoicing systems effectively.
5. What is the future scope of e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia?
E-invoicing is expected to expand into advanced integrations with financial systems, improve data analytics, and contribute to global alignment in tax practices.