Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Types of Retaining Walls
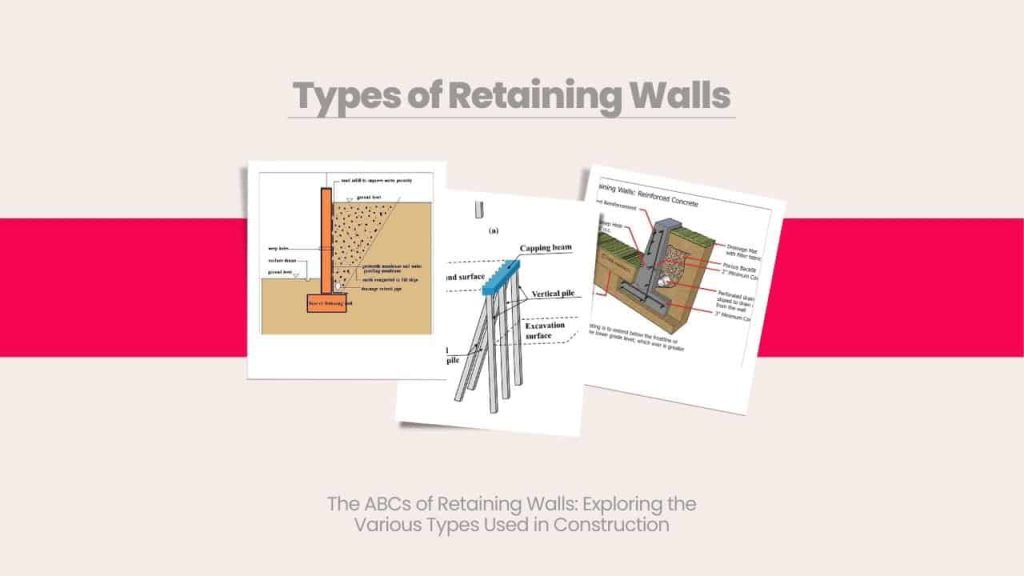
Retaining walls serve the purpose of holding back soil and preventing erosion, while also providing aesthetic appeal to outdoor spaces. There are various types of retaining walls available, each with unique features that make them suitable for different applications. Whether you want to prevent soil erosion in your garden, create more usable outdoor space, or simply enhance the visual appeal of your property, it is essential to understand the different types of retaining walls. In this blog, we will give you a comprehensive overview of retaining walls, including their purpose, benefits, and the different types of retaining walls that you can choose from.
A retaining wall is a structure that is designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion or landslides. Construction projects commonly use retaining walls to create level ground or terraces on sloping sites or protect buildings and infrastructure from soil erosion or damage caused by natural disasters such as flooding or earthquakes.
Why are Retaining Walls used?
- Soil Retention: Retaining walls primarily hold back soil and prevent erosion or landslides. They can help to create the level ground on sloping sites or to protect buildings and infrastructure from soil erosion or damage caused by natural disasters such as flooding or earthquakes.
- Creating Terraces: Retaining walls can create terraces or levels on sloping sites. This can increase the usable space on the site and provide areas for outdoor living, gardens, or recreation.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Retaining walls can be designed to complement the project’s overall design or create a specific aesthetic. They can be made from various materials such as concrete, stone, or wood and can be designed to blend seamlessly into the surrounding landscape.
- Improved Drainage: Retaining walls can be designed with drainage systems to prevent water from accumulating behind the wall. This can help prevent damage to the wall and surrounding structures and improve the overall drainage on the site.
- Structural Support: Retaining walls can support buildings or other infrastructure. They can help distribute the structure’s weight and provide stability to the foundation.
Types of Retaining Walls
Retaining Walls can be broadly classified into two categories:
1) Mechanical Stable Earth Walls
Mechanically stable earth walls provide support and stability to slopes or excavations. They are made of compacted soil, rock, or other materials and resist lateral forces from the soil or other materials.
To construct them, workers place reinforcement material like geotextile fabric on the slope, followed by compacted soil or other material. They repeat this process until the wall is the desired height and thickness. The reinforcement material, such as geogrids, provides tensile strength to the wall and helps distribute lateral forces throughout the structure.
Mechanically stable earth walls are useful in various applications, including road and highway construction, retaining walls, and erosion control. They are especially helpful where construction equipment has limited space or access, or where the soil isn’t suitable for other types of retaining structures. Overall, these walls are a cost-effective and sustainable way to stabilize slopes and excavations, while minimizing environmental impact.
Popular types of Mechanical stable Earth Walls
a) Reinforced Soil Walls
The process of creating reinforced soil walls involves layering soil or other material between reinforcement layers such as geotextiles or geogrids. This provides stability to the soil and distributes lateral forces throughout the structure.
b) Gabion Walls
To construct gabion walls, workers fill wire mesh baskets with rocks, gravel, or other materials. Gabion walls are popular for erosion control purposes because of their flexibility and ability to conform to irregular shapes.
c) Segmental Retaining Walls
Segmental retaining walls consist of interlocking concrete blocks that create a stable structure. They are easy to install and commonly used in residential and commercial applications.
2) Conventional Retaining Walls
Engineers use conventional retaining walls to provide support and stability to soil, rock, or other materials, preventing them from sliding, collapsing, or eroding. These walls find their common usage in construction projects that require level ground on sloped terrain, support structures like buildings or bridges, or prevent soil erosion.
Popular types of Conventional Retaining Walls
a) Gravity Retaining Walls
Gravity retaining walls rely on their weight to resist soil pressure behind them. They are typically constructed from concrete, stone, or masonry, making them ideal for retaining walls up to 3 meters tall. These walls are one of the most common types of conventional retaining walls that rely on their own weight and the weight of the materials they hold back to resist lateral forces. Gravity walls are suitable for shorter walls with smaller loads, made of concrete, brick, or stone.
b) Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever retaining walls are made of reinforced concrete and have an inverted T or L shape. They use the weight of the soil on one side of the wall to counterbalance the weight on the other. These walls are ideal for retaining walls up to 8 meters tall and are commonly used for taller walls or where there are heavier loads. Cantilever walls use a reinforced concrete footing and stem to support a horizontal base, which is anchored to the soil with steel reinforcement bars, creating a cantilever effect to resist the lateral forces.
c) Sheet Pile Retaining Walls
Sheet pile retaining walls are made of steel, vinyl, or wood and are driven into the ground to form a barrier. They are typically used for retaining walls in areas with soft or loose soil, such as near water bodies. Sheet pile retaining walls use steel, vinyl, or wood sheets that are driven into the soil to create a retaining wall. These walls are typically used for temporary structures or walls that are not very tall, often in areas with soft soils or in coastal areas where there is a need to prevent erosion.
4) Anchored Retaining Walls
Anchored retaining walls are reinforced with cables or other support structures that anchor into the soil behind the wall. These walls are suitable for retaining walls over 8 meters in height. They use cables or other tensioning devices to anchor the retaining wall to the soil, making them ideal for taller walls with heavier loads. They can create walls that are up to 50 feet or more in height.
Conclusion
To summarize, retaining walls are crucial structures that serve several purposes, including preventing soil erosion and creating more usable outdoor space. The choice of retaining wall to use depends on various factors, such as the height of the wall, the soil type, and the available space. By comprehending the different types of retaining walls, their features, and their benefits, you can choose the most suitable option for your property. Whether you prefer gravity walls, cantilever walls, sheet pile walls, or anchored retaining walls, a well-built retaining wall will undoubtedly enhance the visual appeal of your property while also serving its practical purpose. With proper design, construction, and maintenance, a retaining wall can last for decades, providing you with peace of mind and long-term value for your property.
Try Onsite, #1 Tool For Site Tracking










