Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Plastering work: Everything You Should Know

The process of applying mortar on rough surfaces such as walls, ceilings, concrete structures, brickwork, etc is called plastering. When plastering is done with good efficacy it provides high strength and smooth finish to the surface. Plastering is done to the interior as well as exterior walls. When plastering work is done on the exterior walls it is called Rendering. The number of coats applied, and the thickness of the plaster layer depends upon the surface of the application. Own a construction business? Onsite is your smart way to manage the construction business.
Free Paint Quantity Calculator: https://onsiteteams.com/paint-quantity-calculator/
Types of Plasters
There are four types of plasters used in construction:
- Gypsum Plaster: The chemical composition of gypsum is calcium sulfate dihydrate. For gypsum plastering, gypsum is mixed with water in a defined proportion. No sand is added to the mix. It is done for interior walls.
- Cement Plaster: When the cement is mixed with sand and water for coating purposes, it is called cement plaster. The ratio of cement: sand for plastering is 1:3 or 1:4. A single coat of cement plaster is sufficient for interior walls. However, 2-3 layers are applied for external walls.
- Lime Plaster: In lime plastering work, the lime is mixed with sand and water. The lime and water are combined in a ratio of 1:1. Sometimes, a small amount of cement is added to improve the strength of the plaster.
- Mud Plaster: This type of plastering involves mixing soil with chopped hep or hay with water. It provides excellent temperature insulation but is less prevalent these days.
Tools Used for Plastering Work
The following tools are used for plastering work:
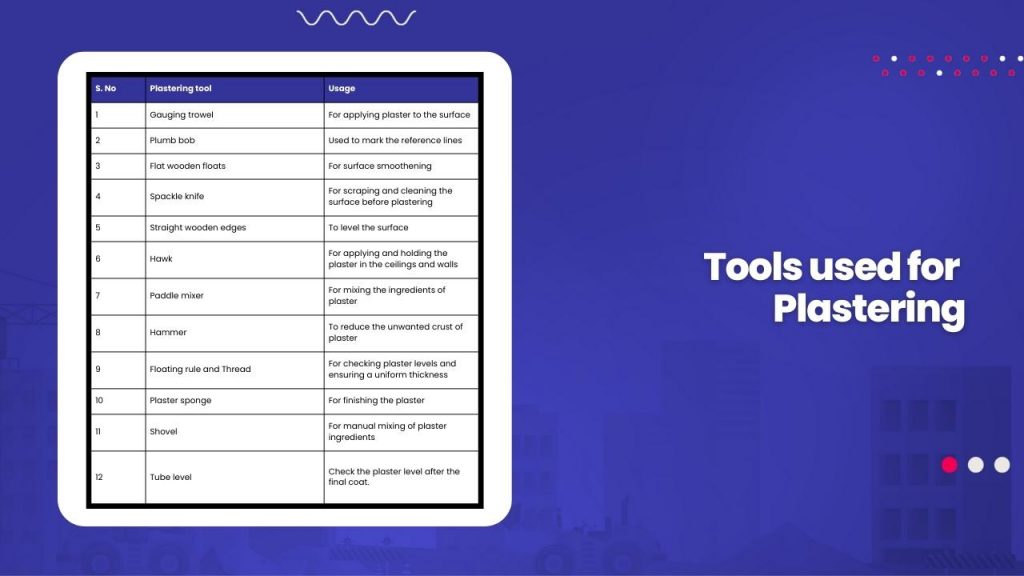
Plastering Work Procedure
The plastering work is carried out through the following process:
1- Surface Work Preparation
The first and foremost of plastering is the preparation of the surface. The surface for plastering is thoroughly cleaned and washed off of any debris or loose particles. The excess cement chunks or crusts are scrapped off with the help of a spackle knife. The mortar joints are cleaned and brushed. Throughout the process of plastering, the surface is kept damp to increase efficiency.
2- Placing Bull Marks & Markings
Bull marks are small plaster patches of thickness 12-15mm placed at a distance of 2m horizontally and vertically from each other. These markings are done to achieve a uniform thickness of the plaster.
3- Bonding
When plastering work is carried out for slabs, columns and beams, hacking is done to improve the bonding effect. The grooves for electric wiring are covered with chicken mesh to avoid cracking.
4- Applying The Base Coat
Water is added to the mortar in adequate proportions to obtain a homogeneous mix. The worker should be mindful of the quantity of mortar mixed for plastering as the mortar sets in 1 hour. For cement plastering, the ratio of cement and sand varies between 1:3 to 1:6, depending on the surface of the application. The base coat is applied with the help of a trowel. The thickness of the base coat should be 12-15 mm for interior walls and 20-25 mm for exterior walls.
5- Applying Subsequent Coats
Usually, multiple coats are applied to exterior walls. Scratches are made on the base coat to increase the bonding of the plastering material. The final skin is finished with floats and a plaster sponge to elevate the aesthetics.
6- Curing
The plastered surface is watered regularly and kept wet for around seven days for curing. Curing enhances the strength of plaster and reduces the risk of cracking and chipping off.
How To Check Plastering Work Quality
- Quality of mortar: Check for the quality of mortar before plastering for the best results. Using a 43-grade or 53-grade cement with recent manufacturing is preferable. Fine sand with a silt content of less than 6% is preferred.
- Check for cracks: The plastered surface should be cured for seven days at least to avoid cracks.
- Check for efflorescence: Some cements contain salts that evaporate on drying of plaster causing the formation of bubbles. This process is called efflorescence. Watering and brushing the plastering work will help get rid of these bubbles.
- Discolouration: This occurs when the mortar water ratio differs in multiple mixes. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain a uniform cement water content throughout the process.
Plastering Work Estimation
Plastering work estimation refers to calculating the quantity of cement and sand needed for plastering. Certain formulas are applied using plastering area, thickness and the ratio of cement and sand to calculate the estimated quantity of mortar.
Plastering Work Design
Decorative designs and artwork with plaster on the external walls of the masonry enhance the appearance of the building. Gypsum plastering work designs on the ceilings, commonly known as false ceilings provide aesthetic looks to the interiors and are thermal insulators. The plastering work cost is 300 Rs per square meter of surface.
Objectives Of Plastering
- It masks poor workmanship, if any, during masonry or concrete build-ups.
- It protects the surface from atmospheric changes and extreme weather conditions.
- It makes the surface more breathable.
- It enhances the aesthetic appeal of interior walls. Plastering work designs are created on the exterior walls and ceilings for a pleasing look.
- It makes the surface ready for painting.

People also search for: plastering defects and their causes, plastering works, plastering work procedure, plastering work in construction, plastering work, scrapped plaster finish, objectives of plastering, defects in plastering, process of plastering






